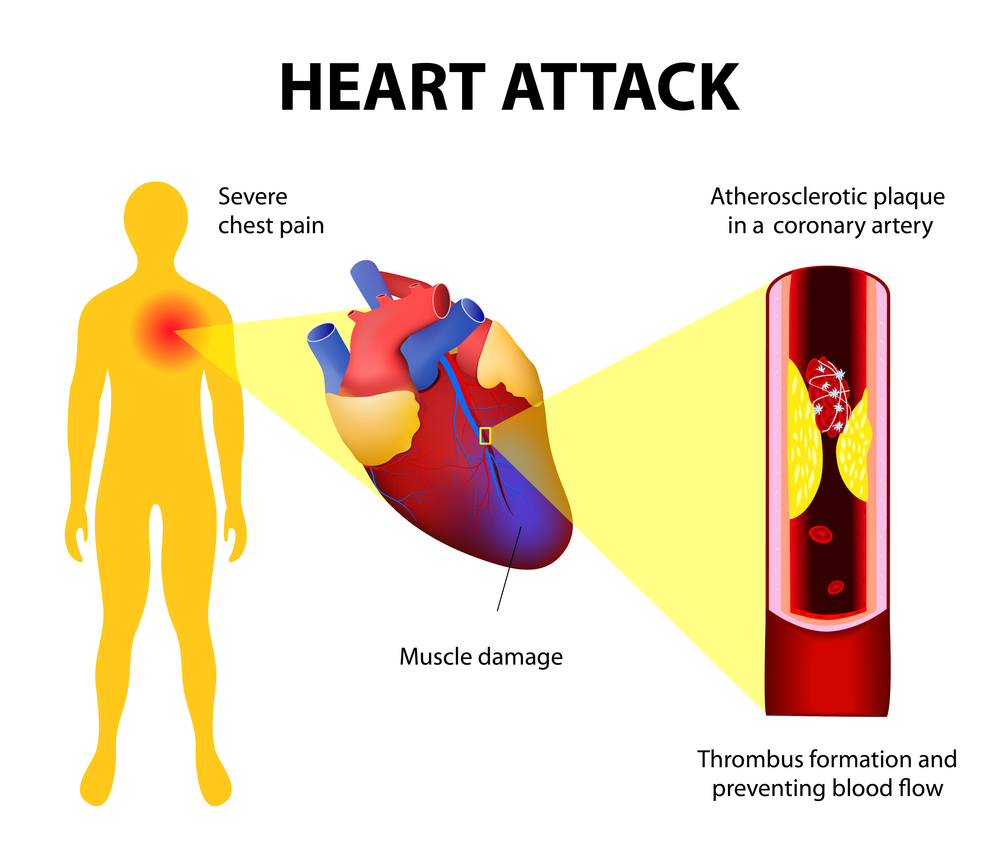
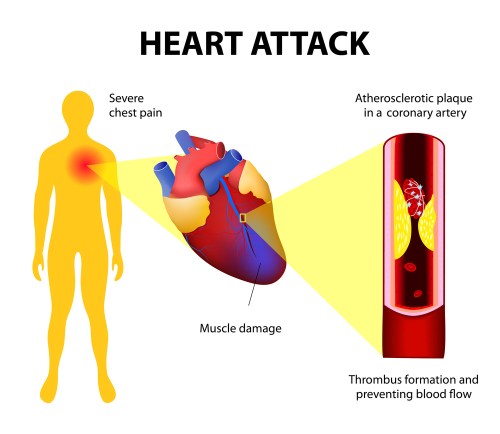
A July 2024 article in the July 31, 2024, Nutrition Journal suggests that artificially sweetened beverage consumption may cause increase risk of death, particularly from cardiovascular disease. From the abstract:
Our systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrated a higher consumption of artificially sweetened beverages in relation to higher risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, whereas no relationship of artificially sweetened beverages with cancer mortality was observed. Compared with the participants in the lowest category of artificially sweetened beverage intakes, those in the highest category had a 13% higher risk of premature death from any cause, and a 26% higher risk of CVD (cardiovascular disease) mortality. Each one additional serving increase in artificially sweetened beverage consumption was associated with 6% and 7% higher risk for all-cause and CVD mortality, respectively. In a dose-response meta-analysis, we also observed a linear association of artificially sweetened beverage consumption with CVD mortality, with a non-linear positive association of artificially sweetened beverages with all-cause mortality. Despite this, substitution of sugary sweetened beverages with artificially sweetened beverages was associated with a lower risk of all-cause and CVD mortality. Various sensitivity analyses and subgroups analyses demonstrated the robustness of the pooled associations. Per NutriGrade, quality of the overall evidence was scored moderate for CVD mortality and all-cause mortality.
Steve Parker, M.D.